Chapter 3
E. Skills for providing education in/through FFS
-
Trying to implement FFS activities immediately turns the sports leader to something more than a simple trainer or coach. They become real educators as their interaction with their team is not only limited to raising their skills in that specific sport, but also using sports as a means to contribute to their personal development and sustainable social transformation. Therefore, it is important to have always in mind that FFS is a process where sport itself becomes a secondary goal to the educational purpose. The skills required to provide education in and through FFS involve a variety of soft skills and competencies:
(a) Understanding the values of FFS:
sports in general are promoting core values and principles that are vital for the personal growth and social development of individuals. Fairness, inclusion, equality, discipline, team work, perseverance, respect, mental and physical health are the foundation of any sport, while FFS additionally enhances mutual support, family bonding, understanding, emotional stability and growth. Therefore, it is important for a sports leader to understand and acknowledge these values and be ready to help their team members recognize and appreciate them. You need to believe in this idea first, before persuading others to believe in it too!
(b) Behavioral capacities:
some of them have been analyzed in details in the previous chapter, but it is definitely worth repeating them here. Effective communication lies once again on the top of the list but that is not all! In order to be able to apply an educational approach to an FFS activity, it is important to be highly motivated and have the capacities to entice your team members into engaging full force into this effort. Of course, this cannot be done without the required leadership skills which will transform you into the authoritative figure in charge of the team’s journey in FFS.
(c) Cognitive skills:
the challenges are not few and we have talked quite a lot about them before. Anything can be overcome though if the person in charge has the skills and strength to make effective decisions and resolve any incidents that could hinder the learning process. It is just as important though to have a clear strategic vision for your educational efforts and this is directly linked to your organizational skills as well: you need to know why you do this, how you do it and what exactly you want to achieve in the end of this journey.
(d) Interpersonal competencies:
this is no news for you…Your FFS team involved different target groups of different age, different role in the family, different backgrounds and –for sure- different characters. You have young and older people, children and adults, guardians and their children, bold or hesitating members, with more or less skills in sports, more or less motivated and engaged. It is important to be able to deal effectively with each one of them and maintain the team’s balance and cohesion. Managing conflicts and resolving misunderstandings is very important and will significantly ease your educational process.
(e) Teaching competencies:
Ah, the complex role of a teacher! You need to combine multiple skills: to assess and coach; to enhance team’s collaboration and support teamwork; to care about your members and ensure inclusion and tolerance; to provide a safe environment for your FFS activities, where “safety” includes physical, mental and psychological security; to be able to pass on the message through your sport activities, explain and support the learning process of your participants.
(f) NFE skills:
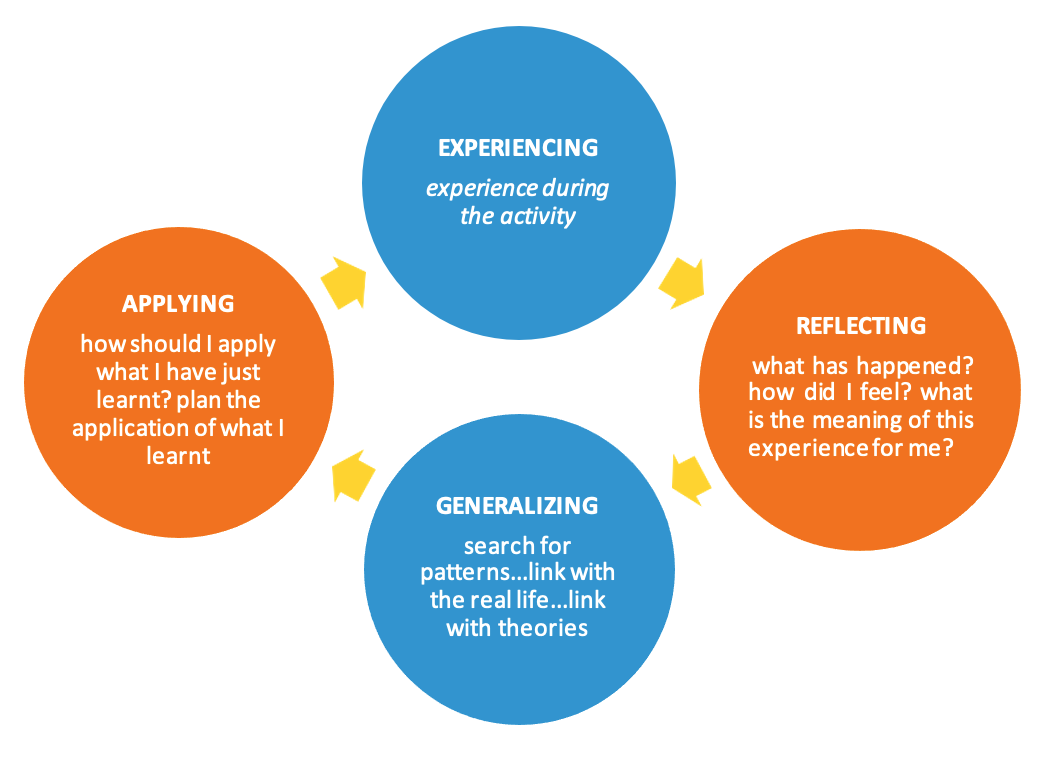
education in and through sports limits out any formal and stereotypical style of learning. Sports activities embrace non-formal education which is defined by the CoE as “planned, structured programs and processes of personal and social education for young people designed to improve a range of skills and competences, outside the formal educational curriculum”[1]. In simple words, NFE methods are learner-centered, enhance experiential learning, boost creativity, are based on involving both individual and group learning with a collective approach, and are organized on the basis if the needs of the participants. Therefore, in order to be able to provide education through sports, one should develop an organized process with educational objectives. In order to understand how NFE methods work, let’s see how A. Huxley defines experiential learning: “Experience is not what happens to you; it is what you do with what happens to you!”. This experiential learning cycle can be presented in the following diagram:
[1] https://www.coe.int/en/web/european-youth-foundation/definitions